Profitability is one of the key metrics that determines a company's success.by: WR Team
Profit Margin is a strong KPI’s to find how your business performs and how much profit your business generates. This KPIs also helps to find which products or services aren’t profitable which help to make informed business decisions.
Higher Net Profit Margin indicates that the company has successfully managed their costs, implemented the right pricing strategy, and practiced efficient management.
Profit Margin = (Net profit / Revenue) x 100
Influence of Foreign Exchange increase or decrease: In emerging markets where interest rates are higher, it is common to observe a devaluation over time. Nevertheless, it can be hard to justify the steep expenses associated with hedging against currency fluctuations when borrowing in these currencies.
Effect of interest rate changes in Profitability
If Ecommerce firms adopts a floating rate interest approach which is best suited for its business. This is because it earns more money when the economy is growing, and interest rates are rising.
How change in Government policy will impact: Government regulations, subsidies, taxes, and tariffs have a crucial impact on profit margins. Examples: Production Linked Incentive benefit will increase 4-6% of sales that cloud increase profit by 30 – 40% (estimated) by considering price advantage over peers. If Power Tariff has increased by 2%, resulting in a rise in electric charges by an additional 10 to 25 paise per unit. This increase will lead to higher operating expenses.
Scenarios 1: A company is incurring net losses, despite reporting positive operating income which concluded that the company has a significant amount of debt.
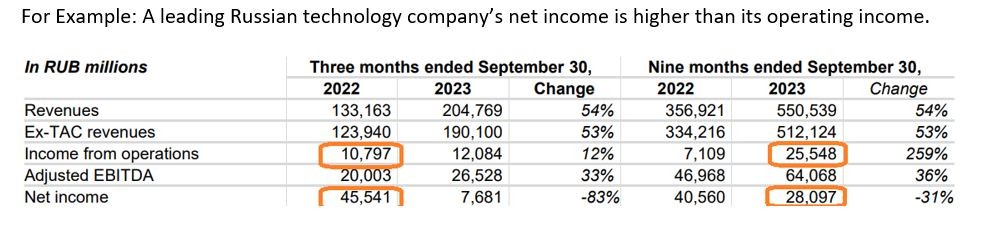
Scenarios 2: In some cases, a company's net income may be higher than its operating income or it may have negative operating income, but it can still have a positive net income. Few reasons will be increase in other sources of income such as investment income, gains from the sale of assets, etc.
For Example: A leading Russian technology company’s net income is higher than its operating income.
In sum, the net profit margin is a measurable tool used by banks and lenders to assess the risk of providing a loan or credit to a company. Similarly, investors use the profit margin to make comparisons between companies of varying sizes in the same industry.